Introduction
Research across the Helmholtz Association (HGF) depends and thrives on a complex network of inter- and multidisciplinary collaborations which spans across its 18 Centres and beyond.
However, the (meta)data generated through the HGF's research and operations is typically siloed within institutional infrastructure and often within individual teams. The result is that the wealth of the HGF's (meta)data is stored and maintained in a scattered manner, and cannot be used to its full value to scientists, managers, strategists, and policy makers.
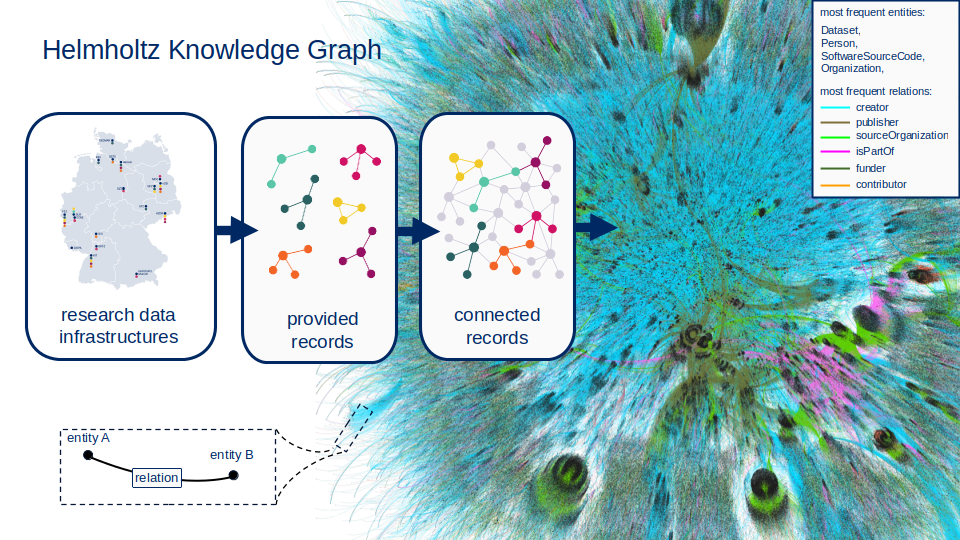
To address this challenge, the Helmholtz Metadata Collaboration (HMC) is launching the unified Helmholtz Information and Data Exchange (unHIDE). This initiative seeks to create a lightweight and sustainable interoperability layer to interlink data infrastructures and provide greater, cross-organisational access to the HGF's (meta)data and information assets. Using proven and globally adopted knowledge graph technology (Box 1), unHIDE will develop a comprehensive association-wide Knowledge Graph (KG) the "Helmholtz-KG": a solution to connect (meta)data, information, and knowledge.
Box 1
What is a Knowledge Graph?
- A "graph", from graph theory, is a structure that models pairwise connections between objects using "nodes" connected by "edges".
- A "knowledge graph" uses such a graph structure to capture knowledge about how a collection of things (represented as nodes) relate to one another (via edges). This helps organisations keep track of their collective knowledge, especially in complex and rapidly changing scenarios.
- Social networks are perhaps the best known graphs, that store knowledge about who knows whom and how, what their interests are, what groups they belong to, and what content they create and interact with.